1. Explain the triple constraint and its importance in project management.
In all organisations there are constraints, the triple constraint refers to three primary variables in any project - time, cost and scope. These three constraints are common to all projects. This is important in project management because each of these three fields are interdependent, meaning that if there if a change in one, it is going to have an effect on the others. It is also important as a projects succes is often judged on these three variables: whether the project cam in on time, within budget and meets the requirements needed.
2. Describe the two primary diagrams most frequently used in project planning.
The two key components to a project plan are project charter and project plan. The charter is a document issued by the project initiator or sponsor that formally authorises the existence of a project and provides the project manager with the authority to apply organisational resources to project activities. It usually contains several sections including:
- Project scope: Defines what work must be completed to deliver a product with the specified features and functions.
- Project objectives: are quantifiable criteria that must be met for the project to be considered a success. Follows a SMART criteria: Specific, Measurable, Agreed upon, Realistic, Time framed.
- Project constraints: Specific factors that can limit options
- Project assumptions: factors that are considered to be true, real, or certain without proof or demonstration.
The project plan is a formal, approved document that manages and controls project execution. It should include the project scope, a list of activities, a schedule, time estimates, risk factors, resources, assignments and responsibilities.
3. Identify the three primary areas a project manager must focus on managing to ensure success.
- People: Resolving conflicts within the team, dealing with both client and workers.
- Managing communications: The project management plan will include a communications plan. The project manager needs to communicate timely, accurate and meaningful information regarding project objectives that involve time, cost, scope and quality and the status of each.
- Managing Change: Whether or not change comes from a crisis or change in market in needs dealt with appropriately.
4. Outline two reasons why projects fail and two reasons why projects succeed.
Where appropriate time planning has not been put into place projects will often end in failure. For a time a project to come in on time, there needs to a detailed stage by stage time frame to work with not just a final deadline to go off. Another reason why projects fail is due to a breakdown in communication between those working on the site and those running the site, where parties are working from incomplete information it will lead to failure as assumptions will be made from a lack of information which will then lead to mistakes
Where a project has been correctly researched and in depth analysis of time and costs has been undertaken a project has a far greater chance of being a success. If a well planned budget and time frame are in place it is easy to fix problems as they occur, rather than trying to fix a problem once it has gotten out of hand. Another essential aspect of project management that will have an affect on the projects success is the change management system they have in place. No matter how much planning, organising and budgeting goes into a project things will still occur that you cannot plan for, a project managers ability to deal with this changes is essential to making project a success
Sunday, May 30, 2010
Week Ten - CRM & BI
1. What is your understanding of CRM?
CRM is concerned with any aspect of the business that will have an affect on the customer and all areas the customer has an affect on. Therefore it is important to see that CRM goes beyond just customer service systems. Whether directly or indirectly as the customer is seen as the most important person in business it is important to give them what they want, and the business should be designed to accomplish that.
2. Compare operational and analytical customer relationship management.
Operational CRM is concerned with the 'face' of the organisation, sections such as marketing, sales and customer service. Any section thathas direct contact with customers in the organisations day-to-day operations. Analytical CRM is more concerned with the collection of data from the operational sectors of the organisation, these back-office operations such as data warehousing and data mining are seen to include all systems that do not deal directly with customers. The division is shown in the diagram:

3. Describe and differentiate the CRM technologies used by marketing departments and sales departments.
Marketing success can be seen as being determined by the organisations ability to gather and analyse the right information, the three CRM technologies marketing uses are :
- List Generators: compiles a list of customer information from a number of sources and then segments the information for different marketing campaigns. The list is the reviewed for potential customers.
- Campaign Management: Guides users through the process of making a marketing campaign helps perform tasks such as definition, planning, scheduling, segmentation and success analysis, can be used to calculate return on investment for certain campaigns.
- Cross-selling/ Up-selling: Selling additional products to customers and increasing the value of a sale made by asking if they want and upgrade.
Sales CRM was the first developments of CRM as it was needed to streamline the process of dealing with customers, it was a method to make all accounts digital and have a storage lace for all customer information. sales also use three primary technologies:
- Sales Management CRM Systems: Automates each phase of the sales process, helping individual sales representatives co-ordinate and organise all of their accounts.
- Contact Management CRM system: maintains all current customer information and identifies prospective customers for future sales.
- Opportunity Management CRM Systems: targets sales opportunities by finding new customers or companies for future sales.
4. How could a sales department use operational CRM technologies?
Sales departments can use operational CRm technologies to maintain the relationship they have established with customers and by fostering the relationship it will lead to a more profitable relationship due to returned business. By using the information gathered sales can also determine the profitable prospective customers and tailor strategies to try and get more of those customers.
5. Describe business intelligence and its value to businesses.
Business intelligence is concerned with the applications and technologies that are used to gather, provide access to and analyse data and information to support decision-making efforts. Through a greater understanding of an organisation's strengths and weaknesses it will become more efficient. Business intelligence is essential to the success of an organisation as it is primarily concerned with having an understanding of the operations undertaken by the organsiation. The provided video gives a further detailed view of the value of business intelligence:
6. Explain the problem associated with business intelligence. Describe the solution to this business problem.
The general problem associated with business intelligence is that companies have invest so much money in to systems such as their customer relationship programs they have begun to have an excessive amount of data. While this collection of data is a good thing, the data is useless unless it is analysed and turned into meaningful information. While ever companies continue to have data being collected and not analysed it is a waste of a resource that should be getting used.
The Solution to this problem is to develop BI systems for workers to make better informed decisions in situations. Through doing this they create an agile intelligent enterprise. Examples of how companies can use BI to make informed decisions are:
- Retail and Sales: Predicting sales; determining correct inventory levels and distribution schedules among outlets; and loss prevention.
- Operations Management: Predicting machinery failure; finding key factors that control optimism of manufacturing capacity.
- Law Enforcement: Tracking crime patterns, locations and criminal behaviour; identifying attributes to assist in solving criminal cases.
7. What are two possible outcomes a company could get from using data mining?
From the use of cluster analysis it is possible for companies to have greater customer segmentation. It can allow a company to segment customer information for customer relationship management systems to help organisations identify customers with similar behavioural traits, such as clusters of best customers or one time customers.
Also by implementing statictical analysis it is possible for comapanies to offer knowledge workers a wide range of powerful statistical capabilities so they can quickly build a variety of statistical models, examine the models assumptions and validity, and compare and contrast the various models to determine the best one for a particular business issue.
CRM is concerned with any aspect of the business that will have an affect on the customer and all areas the customer has an affect on. Therefore it is important to see that CRM goes beyond just customer service systems. Whether directly or indirectly as the customer is seen as the most important person in business it is important to give them what they want, and the business should be designed to accomplish that.
2. Compare operational and analytical customer relationship management.
Operational CRM is concerned with the 'face' of the organisation, sections such as marketing, sales and customer service. Any section thathas direct contact with customers in the organisations day-to-day operations. Analytical CRM is more concerned with the collection of data from the operational sectors of the organisation, these back-office operations such as data warehousing and data mining are seen to include all systems that do not deal directly with customers. The division is shown in the diagram:
3. Describe and differentiate the CRM technologies used by marketing departments and sales departments.
Marketing success can be seen as being determined by the organisations ability to gather and analyse the right information, the three CRM technologies marketing uses are :
- List Generators: compiles a list of customer information from a number of sources and then segments the information for different marketing campaigns. The list is the reviewed for potential customers.
- Campaign Management: Guides users through the process of making a marketing campaign helps perform tasks such as definition, planning, scheduling, segmentation and success analysis, can be used to calculate return on investment for certain campaigns.
- Cross-selling/ Up-selling: Selling additional products to customers and increasing the value of a sale made by asking if they want and upgrade.
Sales CRM was the first developments of CRM as it was needed to streamline the process of dealing with customers, it was a method to make all accounts digital and have a storage lace for all customer information. sales also use three primary technologies:
- Sales Management CRM Systems: Automates each phase of the sales process, helping individual sales representatives co-ordinate and organise all of their accounts.
- Contact Management CRM system: maintains all current customer information and identifies prospective customers for future sales.
- Opportunity Management CRM Systems: targets sales opportunities by finding new customers or companies for future sales.
4. How could a sales department use operational CRM technologies?
Sales departments can use operational CRm technologies to maintain the relationship they have established with customers and by fostering the relationship it will lead to a more profitable relationship due to returned business. By using the information gathered sales can also determine the profitable prospective customers and tailor strategies to try and get more of those customers.
5. Describe business intelligence and its value to businesses.
Business intelligence is concerned with the applications and technologies that are used to gather, provide access to and analyse data and information to support decision-making efforts. Through a greater understanding of an organisation's strengths and weaknesses it will become more efficient. Business intelligence is essential to the success of an organisation as it is primarily concerned with having an understanding of the operations undertaken by the organsiation. The provided video gives a further detailed view of the value of business intelligence:
6. Explain the problem associated with business intelligence. Describe the solution to this business problem.
The general problem associated with business intelligence is that companies have invest so much money in to systems such as their customer relationship programs they have begun to have an excessive amount of data. While this collection of data is a good thing, the data is useless unless it is analysed and turned into meaningful information. While ever companies continue to have data being collected and not analysed it is a waste of a resource that should be getting used.
The Solution to this problem is to develop BI systems for workers to make better informed decisions in situations. Through doing this they create an agile intelligent enterprise. Examples of how companies can use BI to make informed decisions are:
- Retail and Sales: Predicting sales; determining correct inventory levels and distribution schedules among outlets; and loss prevention.
- Operations Management: Predicting machinery failure; finding key factors that control optimism of manufacturing capacity.
- Law Enforcement: Tracking crime patterns, locations and criminal behaviour; identifying attributes to assist in solving criminal cases.
7. What are two possible outcomes a company could get from using data mining?
From the use of cluster analysis it is possible for companies to have greater customer segmentation. It can allow a company to segment customer information for customer relationship management systems to help organisations identify customers with similar behavioural traits, such as clusters of best customers or one time customers.
Also by implementing statictical analysis it is possible for comapanies to offer knowledge workers a wide range of powerful statistical capabilities so they can quickly build a variety of statistical models, examine the models assumptions and validity, and compare and contrast the various models to determine the best one for a particular business issue.
Week Nine - Operations Management and Supply Chain
1. Define the term operations management.
operations Management refers to the management systems in place that convert or transform resources into goods and services. It involves the management of all the core processes that go into manufacturing the goods.
2. Explains operations management's role in business.
Operations management is concerned with all goings on within the business that have affect on the production of the goods, its activities within the business can include:
- Forecasting: Estimating the demand that will be required of the product, whether there will be other circumstances that will have an affect on business.
- Capacity Planning: This is essential to maintain cash flow and increase revenues. If planning is done incorrectly it will cause a shortage or surplus in goods which will have a negative affect on profits.
- Scheduling: The need for the to be a clear understanding of what is to be done and when and by whom.
- Managing Inventory: managing when the goods will be needed, as well as the quantity that will be required.
- Assuring Quality: Maintaining the level of quality needed is essential in all industries
- Motivating and training employees: Making sure goals that are set can be attained and that all employess have necessary training.
- Locating facilities: Where would the correct place for the facility exist, do you want a snow ski hire shop in Cairns.
3. Describe the correlation between operations management and information technology.
IT is relied on by management to give them the needed information to make the correct decisions. By helping operations management make the correct decisions IT helps the business realise its goals and objectives. IT supplies operations management with the necessary to make important decisions within an organisation such as:
- What: What resources will be needed and in what amounts?
- When: When will each resource be needed? When should the work be scheduled? When should material be ordered?
- Where: Where will the work be performed?
- How: How will the product or service be designed? How will the work be done?
- Who: who will perform the work?
4. Explain supply chain management and its role in a business.
Supply chain deals with all of the parties involved, directly or indirectly, in the procurement of a product or raw material. Supply management is concerned with the flow of information between the stages in supply chain and trying to maximise total supply chain effectiveness and profitability.
5. List and describe the five components of a typical supply chain.
- Plan: A startegic section, which deals with the planning of resources needed to meet customer demand.
- Source: The finding of reliable suppliers of goods who are also competitively priced.
- Make: The stage of actual manufacturing of goods and services.
- Deliver: Also known as logistics, plans the effective and efficient delivery of goods and services.
- Return: A problematic stage that must deal with defective goods or returned goods due to excess order returns.
6. Define the relationship between information technology and the supply chain?
The primary role of IT on supply chain management is creating the integrations or tight process and information technology and information linkages between functions within a from such as marketing, sales, finance and between firms, which allows for smooth, synchronised flow of both information and product between customers, suppliers and transportation providers across the supply chain. through the use of IT by supply chain management it integrates planning, decision-making processes, business operating processes and information sharing for business performance management.
operations Management refers to the management systems in place that convert or transform resources into goods and services. It involves the management of all the core processes that go into manufacturing the goods.
2. Explains operations management's role in business.
Operations management is concerned with all goings on within the business that have affect on the production of the goods, its activities within the business can include:
- Forecasting: Estimating the demand that will be required of the product, whether there will be other circumstances that will have an affect on business.
- Capacity Planning: This is essential to maintain cash flow and increase revenues. If planning is done incorrectly it will cause a shortage or surplus in goods which will have a negative affect on profits.
- Scheduling: The need for the to be a clear understanding of what is to be done and when and by whom.
- Managing Inventory: managing when the goods will be needed, as well as the quantity that will be required.
- Assuring Quality: Maintaining the level of quality needed is essential in all industries
- Motivating and training employees: Making sure goals that are set can be attained and that all employess have necessary training.
- Locating facilities: Where would the correct place for the facility exist, do you want a snow ski hire shop in Cairns.
3. Describe the correlation between operations management and information technology.
IT is relied on by management to give them the needed information to make the correct decisions. By helping operations management make the correct decisions IT helps the business realise its goals and objectives. IT supplies operations management with the necessary to make important decisions within an organisation such as:
- What: What resources will be needed and in what amounts?
- When: When will each resource be needed? When should the work be scheduled? When should material be ordered?
- Where: Where will the work be performed?
- How: How will the product or service be designed? How will the work be done?
- Who: who will perform the work?
4. Explain supply chain management and its role in a business.
Supply chain deals with all of the parties involved, directly or indirectly, in the procurement of a product or raw material. Supply management is concerned with the flow of information between the stages in supply chain and trying to maximise total supply chain effectiveness and profitability.
5. List and describe the five components of a typical supply chain.
- Plan: A startegic section, which deals with the planning of resources needed to meet customer demand.
- Source: The finding of reliable suppliers of goods who are also competitively priced.
- Make: The stage of actual manufacturing of goods and services.
- Deliver: Also known as logistics, plans the effective and efficient delivery of goods and services.
- Return: A problematic stage that must deal with defective goods or returned goods due to excess order returns.
6. Define the relationship between information technology and the supply chain?
The primary role of IT on supply chain management is creating the integrations or tight process and information technology and information linkages between functions within a from such as marketing, sales, finance and between firms, which allows for smooth, synchronised flow of both information and product between customers, suppliers and transportation providers across the supply chain. through the use of IT by supply chain management it integrates planning, decision-making processes, business operating processes and information sharing for business performance management.
Week Eight - Networks & Wireless
1. Explain the business benefits of using wireless technology.
Wireless technology now allows business quick and easy access to a greater volume of information than previously possible. Through the implementation of a wireless infrastructure companies have the ability to increase productivity, speed delivery to market and a reduction in operating costs.
2. Describe the business benefits of VoIP.
Voice over IP allows for companies to utilise there internet connection by using them to transmit voice calls. As VoIP makes use of existing technology within companies it allows them to make call more efficiently and more inexpensively than traditional methods. This then gives the company significant cost savings, productivity gains and service enhancements. one of the most popular VoIP options for consumers has been Skype recognisable by there symbol seen below, this service not onlt allows for cheap calls but also video confrencing as well a number of other features.

3. Compare LANs and WANs.
A LAN or Local Area Network is designed to give connectivity to a group of computers that operating within a close proximity of each other such as those at a hospital or university, it is useful for the sharing of files, printers or games. A WAN or Wide Area Network allows ofr connectivity between computers that are spread over a large area such as cities, states or countries. WANs can also be used to connect a number of LAns. In this regard LAns are more approriate for smal business where there is only one location compared to WANs which are more appropriate for organisations that which have a number of locations around the country.
4. Describe RFID and how it can be used to help make a supply chain more effective.
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) uses technology that gives active or passage tags in the forms of chips or smart labels that store unique identifiers for that product which is then relayed to electronic readers. This technology improves the effectiveness of supply chains by having all the information products already stored as electronic data allowing for greater accuracy and understanding of inventory and where products are located through the availability of tracking. through implementation of RFID companies in the future will have much greater access to more detailed and accurate information. The video below discusses the effect of RFID and where RFID may go in the future:
5. Identify the advantages and disadvantages of deploying mobile technology.
Mobile technology gives organisations a range of advantages such as greater accuracy and availability of information. Through the implementation of mobile technologies business wil ocntinue to be competitive as they will have the benefit of greater efficiency and a greater level of communication within the organisation. As well as greater ability for planning the through use of tracking tracking technologies available today.
Disadvantages of mobile networks are that they do allow for greater exposure to other security threats that would not have existed otherwise. Some concerns regard to the ability for people to gather personal information on people including there physical location, which is seen as a risk to their personal safety. Governments have enacted laws to try and protect users auch as the privacy act which exist in Australia.
LINKS
- This links takes you to the Privacy Act of Australia, it shows some of the lengths the government has gone to try and protect users of mobile technology:
http://www.austlii.edu.au/au/legis/cth/consol_act/pa1988108/
Wireless technology now allows business quick and easy access to a greater volume of information than previously possible. Through the implementation of a wireless infrastructure companies have the ability to increase productivity, speed delivery to market and a reduction in operating costs.
2. Describe the business benefits of VoIP.
Voice over IP allows for companies to utilise there internet connection by using them to transmit voice calls. As VoIP makes use of existing technology within companies it allows them to make call more efficiently and more inexpensively than traditional methods. This then gives the company significant cost savings, productivity gains and service enhancements. one of the most popular VoIP options for consumers has been Skype recognisable by there symbol seen below, this service not onlt allows for cheap calls but also video confrencing as well a number of other features.
3. Compare LANs and WANs.
A LAN or Local Area Network is designed to give connectivity to a group of computers that operating within a close proximity of each other such as those at a hospital or university, it is useful for the sharing of files, printers or games. A WAN or Wide Area Network allows ofr connectivity between computers that are spread over a large area such as cities, states or countries. WANs can also be used to connect a number of LAns. In this regard LAns are more approriate for smal business where there is only one location compared to WANs which are more appropriate for organisations that which have a number of locations around the country.
4. Describe RFID and how it can be used to help make a supply chain more effective.
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) uses technology that gives active or passage tags in the forms of chips or smart labels that store unique identifiers for that product which is then relayed to electronic readers. This technology improves the effectiveness of supply chains by having all the information products already stored as electronic data allowing for greater accuracy and understanding of inventory and where products are located through the availability of tracking. through implementation of RFID companies in the future will have much greater access to more detailed and accurate information. The video below discusses the effect of RFID and where RFID may go in the future:
5. Identify the advantages and disadvantages of deploying mobile technology.
Mobile technology gives organisations a range of advantages such as greater accuracy and availability of information. Through the implementation of mobile technologies business wil ocntinue to be competitive as they will have the benefit of greater efficiency and a greater level of communication within the organisation. As well as greater ability for planning the through use of tracking tracking technologies available today.
Disadvantages of mobile networks are that they do allow for greater exposure to other security threats that would not have existed otherwise. Some concerns regard to the ability for people to gather personal information on people including there physical location, which is seen as a risk to their personal safety. Governments have enacted laws to try and protect users auch as the privacy act which exist in Australia.
LINKS
- This links takes you to the Privacy Act of Australia, it shows some of the lengths the government has gone to try and protect users of mobile technology:
http://www.austlii.edu.au/au/legis/cth/consol_act/pa1988108/
Week Seven - Databases and Data Warehouses
1. List, Describe and provide an example of each of the five characteristics of high quality information.
- Accuracy: Is all the information provided correct? For the information to be accurate it must have all the correct information, such as the correct spelling of names and correct numbers used.
- Completeness: Is all teh information needed, provided? Are all the numbers provided for a phone number including area codes, does the address have all the relevant information.
- Consistency: Is all the information consistent throughout the form? Do totals correctly represent the total of individual amounts.
- Uniqueness: Are all the transactions recorded only once or are there duplicates? Has a customer been entered into the system twice?
- Timeliness: Is the information provided up to date with the requirements of the business? does the information need to be updated daily or weekly etc.
2. Define the relationship between a database and a database management system.
The relationship between databases and a database management system (DBMS) is wht allows the raw data from the databases to be turned into meaningful information which can be used to answer queries and manage the database. This information and organisation of databases allows for greater informed business decisions.
3. Describe the advantages an organisation can gain by using a database.
The availability of high quality information greater increase the chances of making a good decision for the organisation as there is a greater understanding of the operations of the organisation. While it cannot guarantee that all decisions will be the a good one, it does ensure that the basis from which decisions are made is accurate. One way of getting such information is by having automatic database storage, the advantages of a system such as this is discussed by the Vice-president of Oracle in the video below:
4. Define the fundamental concepts of the relational database model.
The fundamental concepts or relational database models are entities, entity classes, attributes, keys and relationships. The entity within a relational database model is a person, place or transaction, a table consists of a number of these entities. Entity classes are simply the grouping of similar entities. Attributes or fields refer to the properties of an entity class, for example the attributes of a customer would be their Customer DI and Customer Name. There are two types of keys; primary keys which refer to a field that uniquely identifies a given entity within a table; And a foreign key which in a relational database model is teh primary key of a certain table which appears as another entity within another table. An example of a relational database model can be seen below:
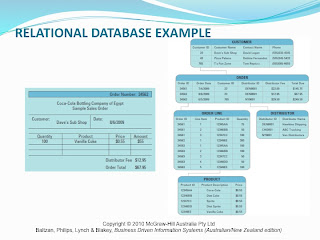
5. Describe the benefits of a data-driven website.
Where a website will be continually and frequently updated and will have a number of contributors a data-driven website is the most appropriate structure. Some advantages include:
- Development: Allows the website owner to make updates/changes at anytime.
- Content Management: Content is easily changeable, which is important when content is being changed regularly
- Future Expandability: It allows for quicker growth and allows other functions or layouts to be changed easily.
6. Describe the roles and purposes of data warehouses and data marts in an organisation.
A data warehouse provides a structure that allows for a logical collection of information gathered from a number of operation databases. It provides organisations with more information to support decision making and business analysis. The data warehouse provides the organisation with a element of summary for the business as instead of showing unnecessary details it may just provide totals and averages.
LINKS
- The link below takes you to an example of a data warehouse, it is the 'Australian Tourism Data Warehouse';
www.atdw.com.au/
- Accuracy: Is all the information provided correct? For the information to be accurate it must have all the correct information, such as the correct spelling of names and correct numbers used.
- Completeness: Is all teh information needed, provided? Are all the numbers provided for a phone number including area codes, does the address have all the relevant information.
- Consistency: Is all the information consistent throughout the form? Do totals correctly represent the total of individual amounts.
- Uniqueness: Are all the transactions recorded only once or are there duplicates? Has a customer been entered into the system twice?
- Timeliness: Is the information provided up to date with the requirements of the business? does the information need to be updated daily or weekly etc.
2. Define the relationship between a database and a database management system.
The relationship between databases and a database management system (DBMS) is wht allows the raw data from the databases to be turned into meaningful information which can be used to answer queries and manage the database. This information and organisation of databases allows for greater informed business decisions.
3. Describe the advantages an organisation can gain by using a database.
The availability of high quality information greater increase the chances of making a good decision for the organisation as there is a greater understanding of the operations of the organisation. While it cannot guarantee that all decisions will be the a good one, it does ensure that the basis from which decisions are made is accurate. One way of getting such information is by having automatic database storage, the advantages of a system such as this is discussed by the Vice-president of Oracle in the video below:
4. Define the fundamental concepts of the relational database model.
The fundamental concepts or relational database models are entities, entity classes, attributes, keys and relationships. The entity within a relational database model is a person, place or transaction, a table consists of a number of these entities. Entity classes are simply the grouping of similar entities. Attributes or fields refer to the properties of an entity class, for example the attributes of a customer would be their Customer DI and Customer Name. There are two types of keys; primary keys which refer to a field that uniquely identifies a given entity within a table; And a foreign key which in a relational database model is teh primary key of a certain table which appears as another entity within another table. An example of a relational database model can be seen below:

5. Describe the benefits of a data-driven website.
Where a website will be continually and frequently updated and will have a number of contributors a data-driven website is the most appropriate structure. Some advantages include:
- Development: Allows the website owner to make updates/changes at anytime.
- Content Management: Content is easily changeable, which is important when content is being changed regularly
- Future Expandability: It allows for quicker growth and allows other functions or layouts to be changed easily.
6. Describe the roles and purposes of data warehouses and data marts in an organisation.
A data warehouse provides a structure that allows for a logical collection of information gathered from a number of operation databases. It provides organisations with more information to support decision making and business analysis. The data warehouse provides the organisation with a element of summary for the business as instead of showing unnecessary details it may just provide totals and averages.
LINKS
- The link below takes you to an example of a data warehouse, it is the 'Australian Tourism Data Warehouse';
www.atdw.com.au/
Week Six - Enterprise Architectures
1. What is information architecture and what is information infrastructure and how do they differ and how do they relate to each other?
A. Information architecture is used to identify where and how imporatant information is stored. Businesses use information architecture to easily store information such as customer records, it is the method used to keep information maintained and secured. The three primary fields that information architecture is concerned with is Backup recovery, Disaster recovery and Information security.
Infrastructure architecture includes the hardware, software and telecommunications equipment that when combined, provides the underlying foundation to support the organisations. Without these systems in place an organisation efficiency would suffer greatly due to lack of necessary technology to get tasks completed. Characteristics of a reliable infrastructure architecture are:
- Flexibility: The ability to adapt to new scenarios and challenges of tomorrow.
- Scalability: Estimating the growth rate of the organisation.
- Reliability: The systems in place are operating correctly.
- Availability: The way in which customers can access the system.
- Performance: The rate at which the system performs certain processes or transactions.
An example of this can been seen in this picture
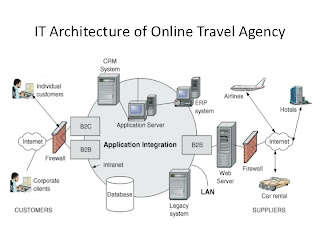
These two systems differ in that information architecture is primarily concerned with just the processes in place not hardware that is necessary for those systems which is what information infrastructure is concerned with. However, both these systems are dependent on each other, an organisation cannot be up to date with it busness practice if it does not have the necessary technology in place as well as the correct operating systems in place.
2. Describe how an organisation can implement a solid information architecture.
By taking the necessary steps to set up systems such as backup recovery, disaster recovery and information security organisation will have the necessary protection required for their information. By having a backup recovery system in place the organisation has the ability get a system up and running after a system crash. It makes this possible by making a copy of the systems information stored at a separate location. Through the implementation of a disiater recovery plan a company can minimise the amount of damage caused by soem kind of disaster such as floods, power outages etc. This plan allows companies to efficiently take action to make steps back towards normal operations again. Information security while being difficult to maintain is extremely important to a businesses success. All organisations need a certain level of protection for there information and hardware. Organisations achieve this through managing user access to system, they do this through the creation of security measures such as usernames and passwords. They also maintain a level of security by having Up-to-date antivirus software and patches.
3. List and describe the five requirement characteristics of infrastructure architecture.
- Flexibility: The ability to adapt to new scenarios and challenges of tomorrow. As well as adapting to business markets the organisation may enter.
- Scalability: Estimating the growth rate of the organisation, and having the ability to adapt to those changes and planning what It requirement will be needed in the future.
- Reliability: The systems in place are operating correctly and only contain correct and accurate information.
- Availability: The way in which customers can access the system, also taking the amount users can access system, whether it is continuosly available or only at certain times.
- Performance: The rate at which the system performs certain processes or transactions. It is also concerned with the being able to adapt the performance changes of the organisation in the future.
4. Describe the business value in deploying a service oriented architecture.
Where an organisation implements a service oriented architecture it allows for greater efficiency. It enables It systems to adapt quickly, easily and economically to support the changes within the business. It allows for communications between different sections of organisation to happen effortlessly, which in turns harbors greater communication between sections of the company. This then adds value to the business by increasing the productivity of the organisation.
5. What is an event?
An event involves the monitoring of the business processes for events that occur which will have some kind of an effect on the organisation such as low inventory warnings or over due shipping order alerts. By doing the correct people are informed automatically when the event occurs.
6. What is a service?
Is a product which has the ability to check information across a number of applications, the product needs to be reusable and also have the ability to be used by a large number of people if it is to have an affect on an organisation.
7. What emerging technologies can companies use to increase performance and utilise their infrastructure more effectively?
One technology that companies are are utilising is 'system virtualisation' by doing this it allows companies to view the material available on one computer as if it were a collection of seperate computers. By doing this businesses have the ability to reduce hardware infrastructure needed which in turn means the company uses less power, making the company 'greener' as well as reducing the companies expenses.
LINKS:
- Some of the key principles of infrastructure architecture:
www.ewita.com/EWITA%20Tools/Strawdogs/SD%20Principles.doc
A. Information architecture is used to identify where and how imporatant information is stored. Businesses use information architecture to easily store information such as customer records, it is the method used to keep information maintained and secured. The three primary fields that information architecture is concerned with is Backup recovery, Disaster recovery and Information security.
Infrastructure architecture includes the hardware, software and telecommunications equipment that when combined, provides the underlying foundation to support the organisations. Without these systems in place an organisation efficiency would suffer greatly due to lack of necessary technology to get tasks completed. Characteristics of a reliable infrastructure architecture are:
- Flexibility: The ability to adapt to new scenarios and challenges of tomorrow.
- Scalability: Estimating the growth rate of the organisation.
- Reliability: The systems in place are operating correctly.
- Availability: The way in which customers can access the system.
- Performance: The rate at which the system performs certain processes or transactions.
An example of this can been seen in this picture

These two systems differ in that information architecture is primarily concerned with just the processes in place not hardware that is necessary for those systems which is what information infrastructure is concerned with. However, both these systems are dependent on each other, an organisation cannot be up to date with it busness practice if it does not have the necessary technology in place as well as the correct operating systems in place.
2. Describe how an organisation can implement a solid information architecture.
By taking the necessary steps to set up systems such as backup recovery, disaster recovery and information security organisation will have the necessary protection required for their information. By having a backup recovery system in place the organisation has the ability get a system up and running after a system crash. It makes this possible by making a copy of the systems information stored at a separate location. Through the implementation of a disiater recovery plan a company can minimise the amount of damage caused by soem kind of disaster such as floods, power outages etc. This plan allows companies to efficiently take action to make steps back towards normal operations again. Information security while being difficult to maintain is extremely important to a businesses success. All organisations need a certain level of protection for there information and hardware. Organisations achieve this through managing user access to system, they do this through the creation of security measures such as usernames and passwords. They also maintain a level of security by having Up-to-date antivirus software and patches.
3. List and describe the five requirement characteristics of infrastructure architecture.
- Flexibility: The ability to adapt to new scenarios and challenges of tomorrow. As well as adapting to business markets the organisation may enter.
- Scalability: Estimating the growth rate of the organisation, and having the ability to adapt to those changes and planning what It requirement will be needed in the future.
- Reliability: The systems in place are operating correctly and only contain correct and accurate information.
- Availability: The way in which customers can access the system, also taking the amount users can access system, whether it is continuosly available or only at certain times.
- Performance: The rate at which the system performs certain processes or transactions. It is also concerned with the being able to adapt the performance changes of the organisation in the future.
4. Describe the business value in deploying a service oriented architecture.
Where an organisation implements a service oriented architecture it allows for greater efficiency. It enables It systems to adapt quickly, easily and economically to support the changes within the business. It allows for communications between different sections of organisation to happen effortlessly, which in turns harbors greater communication between sections of the company. This then adds value to the business by increasing the productivity of the organisation.
5. What is an event?
An event involves the monitoring of the business processes for events that occur which will have some kind of an effect on the organisation such as low inventory warnings or over due shipping order alerts. By doing the correct people are informed automatically when the event occurs.
6. What is a service?
Is a product which has the ability to check information across a number of applications, the product needs to be reusable and also have the ability to be used by a large number of people if it is to have an affect on an organisation.
7. What emerging technologies can companies use to increase performance and utilise their infrastructure more effectively?
One technology that companies are are utilising is 'system virtualisation' by doing this it allows companies to view the material available on one computer as if it were a collection of seperate computers. By doing this businesses have the ability to reduce hardware infrastructure needed which in turn means the company uses less power, making the company 'greener' as well as reducing the companies expenses.
LINKS:
- Some of the key principles of infrastructure architecture:
www.ewita.com/EWITA%20Tools/Strawdogs/SD%20Principles.doc
Monday, April 5, 2010
Week Five Questions - Ethics and Security
1. Explain the ethical issues surrounding information technology.
A.
When information technology is used in a business it faces many of the same ethical issues as the rest of the business, including privacy, accurate data records and property. However they do need to be put into an information technology realm. Examples of ethical issues involving information systems include; Intellectual property, where an employee designs and develops an idea or product for a company, who owns the intellectual property of the idea? It also includes the monitoring of employees while at work to make sure that only properly licensed software is being used by the company, or if they are using someone else's intellectual property there are proper ways for the use to be reported. This monitoring of employees can however cause problems with employee privacy.
2. Describe the relationship between an 'email privacy policy' and 'internet use policy'
A.
A privacy policy that a company has in place describes how certain systems are to be used and the right of the company to have access to your information at work. A clear example of this would be the policy a company has in place in regard to emails at work, for example a companies policy may outline that they have the right to check your emails at anytime, although it will not be done unless suspicion has been raised. The policy may also go into details such as forbidding employees from using internal mail lists for spam emails, for things such as goods for sale.
The 'internet use policy' on the other hand regulates the way in which employees use the internet while they are at work. This policy may forbid employees from looking at non-work related websites or from using social networking websites for personal use. The policy may also go into detail forbidding employees from using the internet at work to run their own online business.
3. Summarise the five steps to creating an information security plan.
A.
- Develop the information security policies
Identifies who is responsible and accountable for designing and implementing the organisation's information security policies. This can include implementing rules such as mandatory logging off for breaks or putting in an automatic sign off after 5 minutes of inactivity.
- Communicate the information security policies.
Train all employees on the policies and establish clear expectations for following the polices. An example of this can be the issuing reprimands to employees who leave computers unsecure.
- Identify critical information assets and risks.
Require the use of user IDs, passwords and anti-virus software on all systems. Also have necessary firewalls on all computers that have external links. The inclusion of intrusion detection software allows for attacks to be identified quickly and responded to.
- Test and re-evaluate risks.
Continually perform security reviews, audits, background checks and security assessments. This testing can be done by a third party company, who can then continue with the on-going maintenance of the system.
- Obtain stakeholder support
Gain the approval and support of the information security policies from the board of directors and all stakeholders.
4. What do the terms; authentication and authorization mean, how do they differ, provide some examples of each term.
A.
Authentication refers to proving who you are. It can be either something the user is such as facial recognition or retina scans, something the user knows such as a user ID and password or something that the user has such a smart card or token card.
Authorization is concerned with the level of access you have once you are within the system. Once you have authenticated who you are then you will have a level of authorization which determines what you are allowed to have access to. Examples of this would be those that are not in the accounting department may not have authorization to have access to he financial records.
5. What are the Five main types of Security Risks, suggest one method to prevent the severity of the risk?
A.
- Human error.
To minimise the damage that can be done from this risk a company should put in the necessary training programs for all employees that could possibly use the system.
- Technical failure.
Where a technical failure occurs have adequately trained professionals on hand to deal with the problem. This will minimise the time the system is down and decrease the cost as well as the amount of time the system is unprotected.
- Natural disaster.
Where an unforeseeable natural disaster occurs a company should have the necessary back ups and disaster recovery systems in place to minimise the damage.
- Deliberate act.
This is caused by spam, spyware or sabotage by an employee. This can be dealt with by giving employees the necessary training on how to handle spam and spyware on their computer. Companies can try to avoid sabotage by employees by running background checks as well on-going monitoring of employee activities.
- Management failure.
By enforcing that all the necessary training is done down the management hierarchy, it will limit the damage that will be done by management failure. By also having an adequate reporting system to clearly show when the necessary training has been done.
A.
When information technology is used in a business it faces many of the same ethical issues as the rest of the business, including privacy, accurate data records and property. However they do need to be put into an information technology realm. Examples of ethical issues involving information systems include; Intellectual property, where an employee designs and develops an idea or product for a company, who owns the intellectual property of the idea? It also includes the monitoring of employees while at work to make sure that only properly licensed software is being used by the company, or if they are using someone else's intellectual property there are proper ways for the use to be reported. This monitoring of employees can however cause problems with employee privacy.
2. Describe the relationship between an 'email privacy policy' and 'internet use policy'
A.
A privacy policy that a company has in place describes how certain systems are to be used and the right of the company to have access to your information at work. A clear example of this would be the policy a company has in place in regard to emails at work, for example a companies policy may outline that they have the right to check your emails at anytime, although it will not be done unless suspicion has been raised. The policy may also go into details such as forbidding employees from using internal mail lists for spam emails, for things such as goods for sale.
The 'internet use policy' on the other hand regulates the way in which employees use the internet while they are at work. This policy may forbid employees from looking at non-work related websites or from using social networking websites for personal use. The policy may also go into detail forbidding employees from using the internet at work to run their own online business.
3. Summarise the five steps to creating an information security plan.
A.
- Develop the information security policies
Identifies who is responsible and accountable for designing and implementing the organisation's information security policies. This can include implementing rules such as mandatory logging off for breaks or putting in an automatic sign off after 5 minutes of inactivity.
- Communicate the information security policies.
Train all employees on the policies and establish clear expectations for following the polices. An example of this can be the issuing reprimands to employees who leave computers unsecure.
- Identify critical information assets and risks.
Require the use of user IDs, passwords and anti-virus software on all systems. Also have necessary firewalls on all computers that have external links. The inclusion of intrusion detection software allows for attacks to be identified quickly and responded to.
- Test and re-evaluate risks.
Continually perform security reviews, audits, background checks and security assessments. This testing can be done by a third party company, who can then continue with the on-going maintenance of the system.
- Obtain stakeholder support
Gain the approval and support of the information security policies from the board of directors and all stakeholders.
4. What do the terms; authentication and authorization mean, how do they differ, provide some examples of each term.
A.
Authentication refers to proving who you are. It can be either something the user is such as facial recognition or retina scans, something the user knows such as a user ID and password or something that the user has such a smart card or token card.
Authorization is concerned with the level of access you have once you are within the system. Once you have authenticated who you are then you will have a level of authorization which determines what you are allowed to have access to. Examples of this would be those that are not in the accounting department may not have authorization to have access to he financial records.
5. What are the Five main types of Security Risks, suggest one method to prevent the severity of the risk?
A.
- Human error.
To minimise the damage that can be done from this risk a company should put in the necessary training programs for all employees that could possibly use the system.
- Technical failure.
Where a technical failure occurs have adequately trained professionals on hand to deal with the problem. This will minimise the time the system is down and decrease the cost as well as the amount of time the system is unprotected.
- Natural disaster.
Where an unforeseeable natural disaster occurs a company should have the necessary back ups and disaster recovery systems in place to minimise the damage.
- Deliberate act.
This is caused by spam, spyware or sabotage by an employee. This can be dealt with by giving employees the necessary training on how to handle spam and spyware on their computer. Companies can try to avoid sabotage by employees by running background checks as well on-going monitoring of employee activities.
- Management failure.
By enforcing that all the necessary training is done down the management hierarchy, it will limit the damage that will be done by management failure. By also having an adequate reporting system to clearly show when the necessary training has been done.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)